

The development of these kind of relationships is in full expansion and become indispensable (useful) in pharmaceutical chemistry and drug design. The quantitative structure-activity Relationship (QSAR) study is the process by which a molecular structure is correlated with a well-determined effect such as biological activity or chemical reactivity. In order to get new compounds with more interesting biological activities the condensation of the Dapsone with 2-azetidinone was therefore envisaged by some chemists. In recent years, the synthesis of 2-azetidinones and the study of their antibacterial properties have permitted to obtain compounds with various pharmacological activities such as antidiabetic activity, anti-inflammatory and Anti-HIV activity. It includes penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems, nocardicins, monobactams, clavulanic acid, sulbactams and tazobactams, which have been widely used as chemotherapeutic agents to treat bacterial infections and microbial diseases. The 2-azetidinone (β-lactam) ring system is the common structural feature of a certain number of β-lactam with broad antibiotic spectrum. In such a context the continuation of the development of new more efficient Dapsone derivatives is a real necessity.
It shows resistances during treatment too.
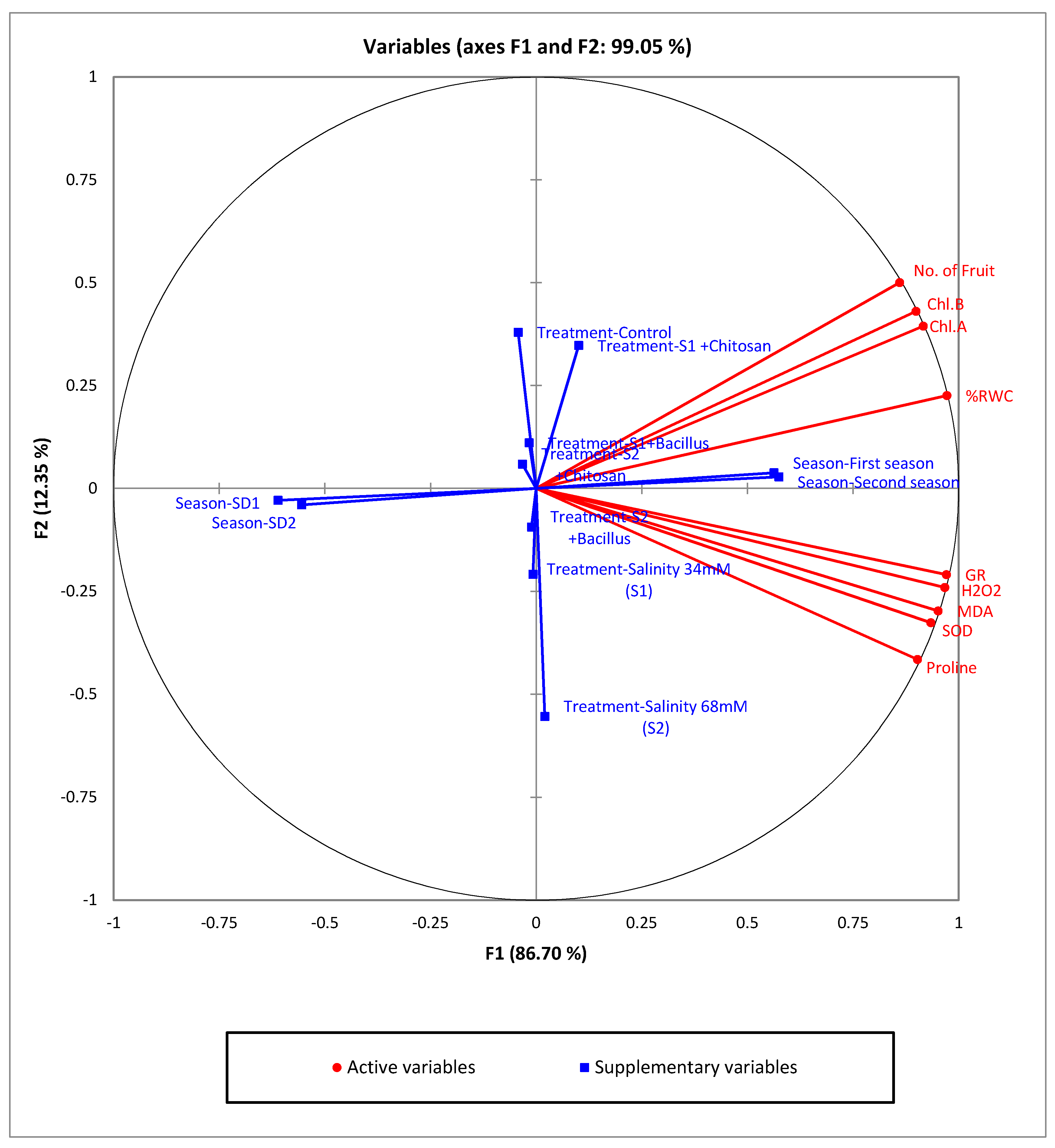
However, nowadays Dapsone presents many undesirable effects such as cutaneous, neurological and psychiatric infections. Introductionĭiamino-Diphenyl sulfone or DDS (Dapsone) is a biologically active sulfone (bacteriostatic) used in the treatment of leprosy. External validation sets also verified all the Tropsha et al. acceptance criteria used for the test set are verified. Moreover, the index of electrophilic is the first descriptor in terms of priority for the prediction of the antibacterial activity of the studied compounds. The quantum descriptors of electrophilic index ( ω), electronic energy ( ε 0) and dipole moment (μ) are responsible of the antibacterial activity of the Azetidinones derived from Dapsone. So these models have good statistical performances. Those of the second model linked to the activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa are the regression coefficient R 2 = 0.933, the standard deviation S=0.135, the Statistical significance of regression, Fisher F-test F = 46.582 and the cross-validation coefficient Q 2cv= 0.928. The different statistical indicators of the first model which are as a function of the Bacillus subtilis activity are the coefficient of determination R 2= 0.945, the standard error of the regression S = 0.139, the Statistical significance of regression, Fisher F-test F = 94.315 and the cross-validation correlation coefficient Q 2cv=0.942. The molecular descriptors were obtained by applying the methods of quantum chemistry at the B3LYP/6-31G (d) level. It allowed to obtain two different models according to the molecular descriptors and the antibacterial activities ( Bacillus subtilis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa).
Xlstat 2014.5.03 older version series#
This QSAR study was conducted by using a series of Azetidinones which belong to Dapsone derivatives.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
